Understanding Severe Atopic Dermatitis and its Treatment Options
Understanding Severe Atopic Dermatitis and its Treatment Options
Atopic dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that affects millions of people worldwide. While most cases of atopic dermatitis are mild to moderate in severity, there is a subset of individuals who suffer from severe atopic dermatitis, which can significantly impact their quality of life. In this article, we will delve into the causes, symptoms, and available treatment options for severe atopic dermatitis.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of atopic dermatitis is still not fully understood. However, it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. People with a family history of atopic dermatitis, asthma, or hay fever are more likely to develop the condition. Additionally, certain triggers such as allergens, irritants, stress, and climate changes can exacerbate the symptoms of atopic dermatitis.
Symptoms
Severe atopic dermatitis presents with more intense and persistent symptoms compared to milder forms of the condition. The most common symptoms include:
- Intense itching
- Redness and inflammation of the skin
- Dry and scaly skin
- Cracked and oozing skin
- Thickened and leathery skin
- Sleep disturbances
- Impaired quality of life
These symptoms can appear anywhere on the body but are most commonly found on the face, neck, and extremities.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing severe atopic dermatitis requires a thorough evaluation by a dermatologist or allergist. The healthcare provider will examine the affected areas of the skin and inquire about the patient’s medical history and family history of atopic conditions. In some cases, additional tests such as patch testing or skin biopsy may be performed to rule out other skin disorders or identify specific triggers that worsen the symptoms.
Treatment Options
While there is no cure for severe atopic dermatitis, several treatment options are available to manage the symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life. The treatment plan may vary depending on the individual’s age, overall health, and the severity of their condition. Some common treatment approaches include:
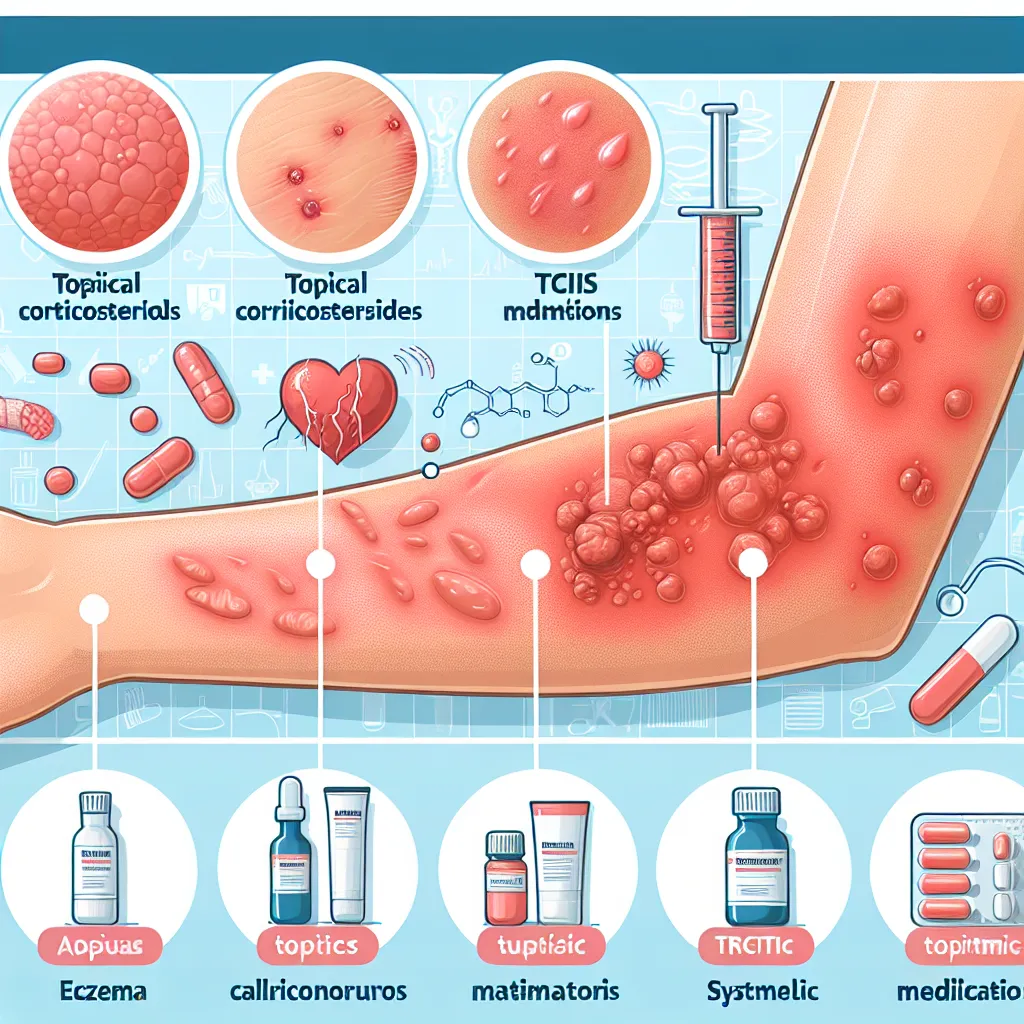
1. Topical Medications
Topical corticosteroids are the most commonly prescribed medications for atopic dermatitis. They work by reducing inflammation and relieving itching. In severe cases, stronger corticosteroids may be prescribed, but long-term use of high-potency steroids should be avoided to prevent potential side effects.
Other topical medications, such as calcineurin inhibitors (e.g., tacrolimus, pimecrolimus), may be used as alternatives or in combination with corticosteroids. These medications help suppress the immune response and reduce inflammation.
2. Systemic Medications
In cases where topical treatments are ineffective or not feasible, systemic medications may be prescribed. These medications are taken orally or by injection and work throughout the body to reduce inflammation and control the immune response. Examples of systemic medications for severe atopic dermatitis include oral corticosteroids, cyclosporine, methotrexate, and dupilumab (a newer biologic medication).
3. Wet Wrap Therapy
Wet wrap therapy involves applying moisturizers or topical medications to the affected areas and then covering them with wet bandages or clothing. This technique helps hydrate the skin, reduce itching, and enhance the absorption of medications. It is particularly useful for severe flare-ups or when the skin becomes extremely dry and cracked.
4. Phototherapy
Phototherapy, also known as light therapy, involves exposing the skin to controlled doses of ultraviolet A (UVA) or ultraviolet B (UVB) light. This treatment helps reduce inflammation, suppress the immune response, and alleviate itching. Phototherapy is usually administered in a healthcare facility under medical supervision.
5. Biologic Medications
Biologic medications are a newer class of drugs that target specific molecules involved in the inflammatory process of atopic dermatitis. Dupilumab is currently the only FDA-approved biologic medication for the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in adults and children aged 12 and older. These medications are typically reserved for individuals who have not responded to other treatment options or have severe, uncontrolled symptoms.
Lifestyle and Self-Care Measures
In addition to medical treatments, individuals with severe atopic dermatitis can adopt certain lifestyle changes and self-care measures to manage their condition more effectively. These include:
- Keeping the skin well-moisturized with fragrance-free moisturizers
- Avoiding harsh soaps, detergents, and other irritants
- Wearing loose-fitting, breathable clothing made of soft fabrics
- Using mild, fragrance-free laundry detergents
- Avoiding scratching or rubbing the affected areas
- Maintaining a healthy diet and managing stress levels
Conclusion
Severe atopic dermatitis can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, but with proper diagnosis, treatment, and self-care, the symptoms can be effectively managed. It is essential to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses the unique needs and challenges associated with severe atopic dermatitis. By staying informed and taking proactive measures, individuals with this condition can lead fulfilling lives free from the burden of severe atopic dermatitis.
